Blogs
Enhancing the Abilities of Healthcare SectorOverstating the importance of Artificial Intelligence is difficult. When implemented efficiently, AI holds the capacity to boost your billing business tenfold. In many cases, AI is the thing that is scaling the business rather than the physical workforce. The question on many business minds is how does AI change the way business is done?
To help answer this question we analyzed many billing and coding companies. Below is a summarized version of our findings from the research:
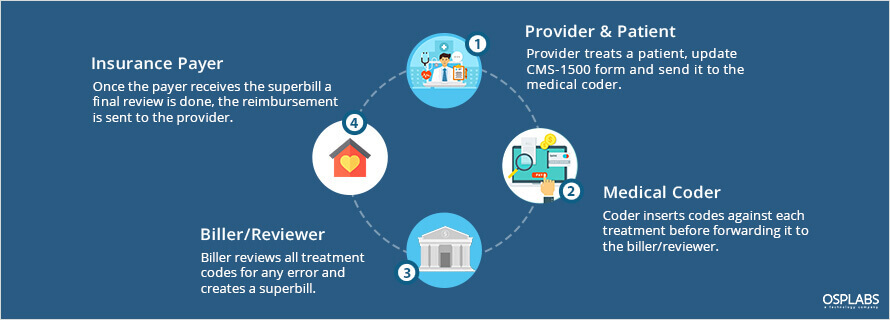
The traditional billing system involves a lot of manual documentation and paperwork. The paper claim is a time-taking process where coders entered each code individually in the printed forms. All the paper forms are then passed to the medical billing organization and later to the payers.
In a paper-based setup, the average turnaround time from filing a claim to receiving payments is between 5 to 7 weeks whereas in automated medical billing systems can be reduced to 2 weeks.

Today, the ongoing challenge is the coding accuracy. To improve the efficiency and efficacy of billing and coding process, many healthcare companies are finding ways to simplify manual coding labor with AI applications.
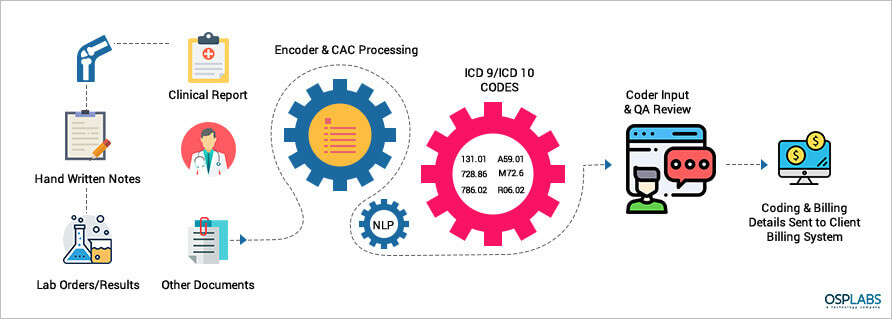
The emerging technology in AI is based on Computer Assisted Coding (CAC) which works on Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP). The CAC automatically identify and extract data from documents and insert into the system.
The need of the hour is an automated web-based system that analyzes physician documentation for the text/treatment and automatically recognizes relevant medical codes.
Beyond processing codes and high volumes of data, AI can significantly reduce the standard work hours and human error.
A natural concern of the popularity of AI applications is the fear, within the industry, that these emerging technologies will shrink the number of jobs available in the medical billing and coding spectrum.
It must be noted, however, that these applications come with the ability to substantially increase the efficiency and speed of human coders to undertake accurate coding but cannot entirely replace human coders. For example, when the coder makes a mistake, the application can immediately point it out with recommendations to rectify the error, and the correction is made as fast as possible. This takes care of the ‘too late’ issues and increases the speed at which the coder works.
Nonetheless, it is worthy of mentioning that this concern can be mitigated by looking at the targeted growth rate of employment within the healthcare sector is at an unprecedented rate over the next decade. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects an 18 percent boost in employment for health information technicians between 2016 and 2026, far above the average growth rate for all other occupations, adding 2.4 million new jobs. (2)
The complex nature of medical billing and coding makes it a constant target of errors and sometimes, these can result in a considerably high loss.
This complexity also lends itself toward the requirement of a more significant workforce, where coders are spending more and more time executing menial tasks that could be undertaken swiftly and efficiently by automated systems of AI technologies.
Considering the current growth of this aspect of healthcare and its expected rise in the U.S., a robust system is the need of the hour.
AI automation is that system, which is poised to address all the pain points that the current system is experiencing, such as inaccurate billing instance, etc.
Considering that the rectification of erroneous billing, when done manually, is a lengthy and complicated procedure that can incur further costs, adoption of AI can automatically point out the errors immediately and mitigate those added costs and time consumption.
Medical billing and coding is the essential component of how healthcare is delivered and reported in the U.S. Inaccurate coding is a challenge that needs to be addressed with new technology. OSP Labs is working with health technologists to build impacting solutions for medical coding companies.
Schedule a quick online appointment with our AI specialist to dive deep into intelligence healthcare claim management and see some of our innovative AI projects. We analyze your business, understand your pain points and create an AI roadmap to solve your critical challenges.
Considering the current growth of this aspect of healthcare and its expected rise in the U.S., a robust system is the need of the hour.